DMMS.EDU – a resource for diabetes education
The DMMS.EDU© (Diabetes Mellitus Metabolic Simulator for Education) is the first simulation environment designed to demonstrate glucose response in people with T1, T2, or Pre-diabetes mellitus. It is the home of over 50 virtual subjects who can be “treated” with diet, exercise and medication and is ideal for examining treatment and lifestyle impact on glucose control.
Modeling and simulation of diabetes drugs and treatments can provide a visual understanding regarding:
- The relationship between carbohydrate in meals and blood glucose changes over the day for better understand of post-prandial hyperglycemia
- Comparison of a current treatment plans to a proposed treatment that includes adjusted diet and exercise, to evaluate and demonstrate potential improvement in blood glucose variability and HbA1c levels
- Comparison of glucose control with insulin treatment compared to oral medication for subjects who would benefit from transition to insulin
- The relationship between meals, exercise and the potential for hypoglycemia during the daytime or at night
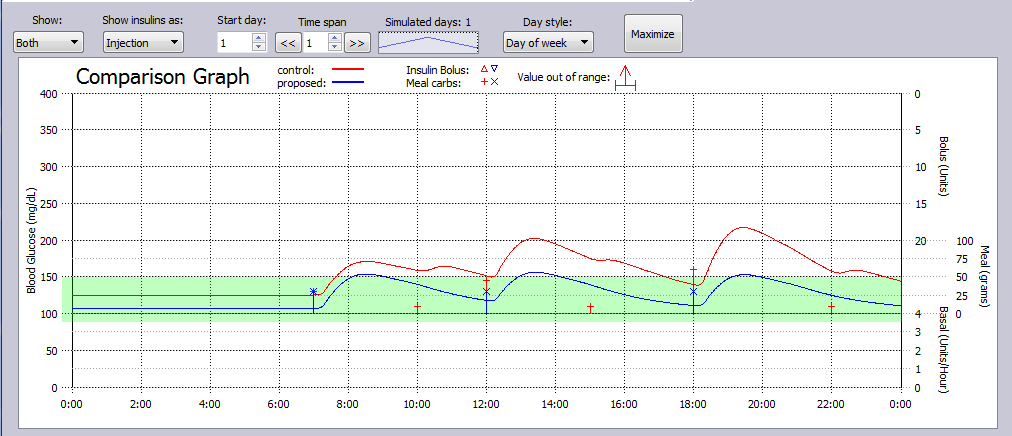
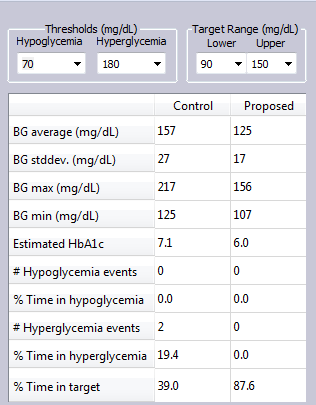
In this simulation Example, a T2DM subject simply dropped snacking between meals, and took 1000 mg Metformin daily to achieve improved glucose control.
The glucose levels for both control and proposed treatment plans are shown in the metrics table.
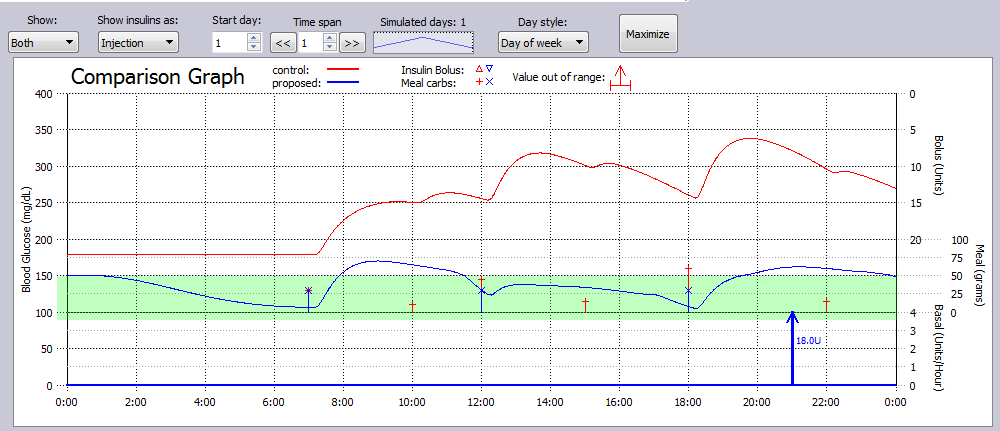
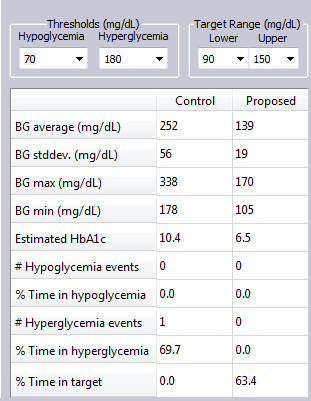
In this simulation Example, a T2DM subject not only dropped snacks, but lowered their CHO intake at meals, and added exercise daily, as well as parked farther from work and walked 15 minutes to and from work on this day.
The glucose metrics improved significantly for this subject with these changes.
While these simulations may not reflect the individual patient’s response, they are able to see potential impact of similar changes to their personal lifestyle choices.
The subject parameters include insulin blood levels and insulin sensitivities that are consistent with human populations based on clinical studies (Dalla Man 2007). The lifestyle models are based on the results of human studies examining exercise, mixed meals, and circadian rhythm, while the medication models are designed from Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamics of the drugs such as long and rapid acting insulin and metformin.
The DMMS.EDU can be easily programmed to demonstrate the results of not managing various daily lifestyle habits compared to glucose control achieved by improved self-management practices with optimized lifestyle and medical treatment adjustments. It will change how patients see their diabetes.
The DMMS.EDU can be easily programmed to demonstrate the results of not managing various daily lifestyle habits compared to glucose control achieved by improved self-management practices with optimized lifestyle and medical treatment adjustments. It will change how patients see their diabetes.
The DMMS.EDU is provided with in silico subject populations that represent the variability found in real-world populations. The cohorts include:
DMMS.EDU is unique in that it uses simulation to demonstrate the types of outcomes that may result from various lifestyle and treatment choices. Features include:
- User-friendly, intuitive user input and data display with “tool-tip” support.
- Support for Type 1, Type 2 and prediabetic conditions in a single compact format.
- Easy subject selection to best match patient parameters.
- Both graphical and tabular comparison of control versus proposed treatment plan, signal outputs and derived statistics.
- User-defined simulation duration: A single day, or up to three months.
- Support for anti-diabetic drugs with complete control of dosing (times and quantities).
- Support for both basal (continuous or long-acting) and rapid-acting bolus insulin injections.
- Support for both meal boluses and correction boluses. (Correction boluses may be meal-based or alarm-based.)
- Meals and exercise patterns (timing and quantity) defined for each day of the simulation.
- All results (signal outputs, comparison graphs, statistics) may be saved in data files for later reference.
- Treatment plans may be saved in files so that simulations can be repeated, either as-is or with modifications.
- Extensive user’s manual with repeatable examples.
TEG offers further validation of internal in-silico study results through simulation services using the 100 subject, FDA-accepted populations. TEG will work with the client to provide custom modeling of devices and drugs, and designing clinical protocols to the client’s specifications.
Simulation results from the FDA-accepted virtual populations can be submitted to the FDA as a pre-clinical study for IDE or 510K approval of new devices, as preliminary data for IND of new drugs or for assessment of bio-equivalence.
